
Work Psychology: Unlocking Human Potential in the Modern Workplace
Work psychology, also known as organisational or industrial psychology, is the key to understanding the human experience at work. In today’s dynamic workplace—shaped by rapid technological advancements, flexible work arrangements, and the evolving gig economy—understanding this field is more crucial than ever. This exploration delves into the core principles of work psychology, offering practical insights and real-world examples to help you navigate the complexities of the modern professional landscape and create thriving, productive environments.
Understanding the Individual in the Workplace: A Psychological Perspective
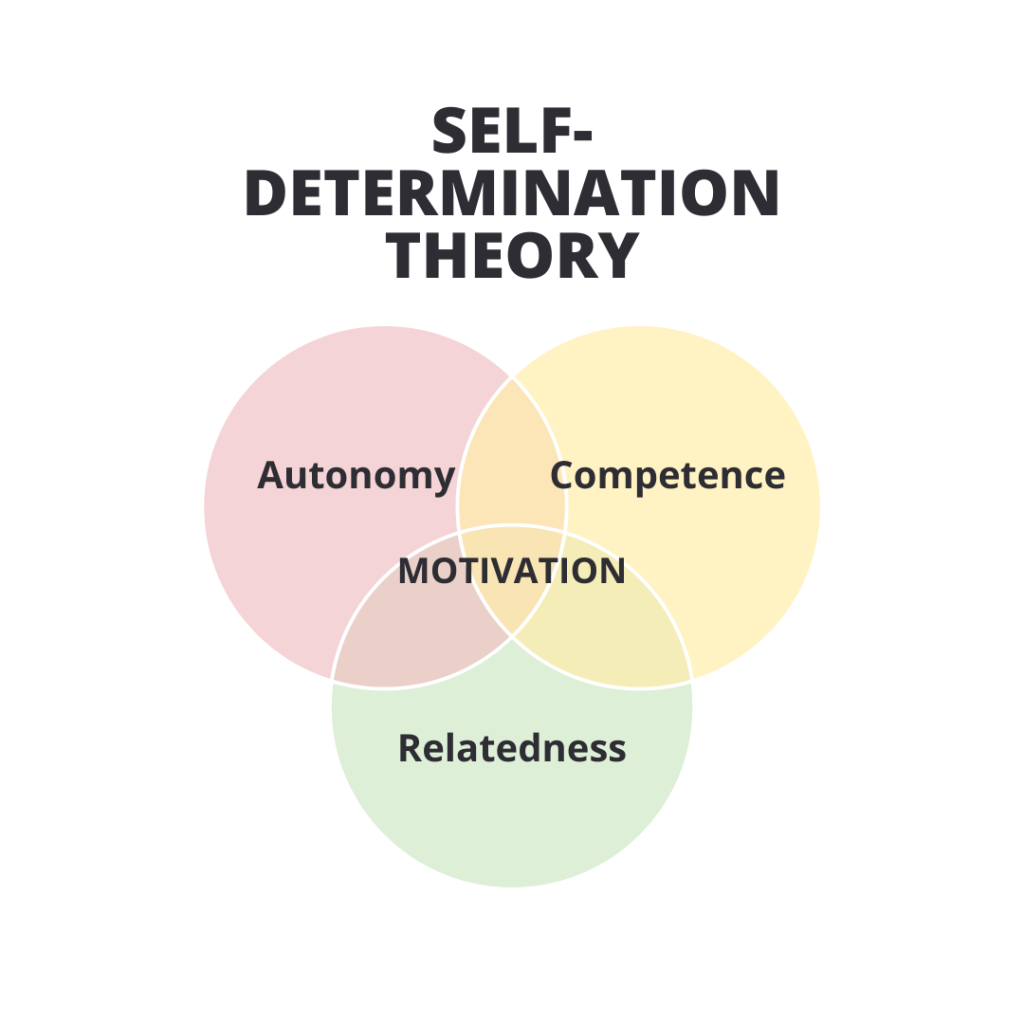
Work psychology goes beyond simply maximising efficiency. It delves into the psychological processes underlying motivation, job satisfaction, engagement, and well-being. For example, Self-Determination Theory suggests that fulfilling employees’ needs for autonomy, competence, and relatedness boosts intrinsic motivation. Google, known for its employee-centric culture, empowers employees with autonomy and opportunities for growth, aligning with these principles. Understanding these individual factors allows organisations to tailor their approach to maximise employee engagement and performance.
 Navigating the 21st-Century Workforce: Diversity, Inclusion, and Technological Change
Navigating the 21st-Century Workforce: Diversity, Inclusion, and Technological Change
Today’s workforce is increasingly diverse, spanning generations, cultures, and levels of technological expertise. Work psychology provides the tools to navigate this complexity. For instance, Hofstede’s cultural dimensions theory helps organisations understand how cultural differences influence workplace communication and collaboration. Moreover, as automation transforms industries, work psychology guides the development of reskilling and upskilling programs. By embracing diversity and fostering inclusive practices, organisations can create a dynamic and innovative workforce.
Designing Human-Centered Work Environments: Ergonomics and Human-Machine Interaction
The workplace environment significantly impacts employee well-being and productivity. Ergonomics, focused on designing user-friendly workspaces, plays a crucial role. Google, renowned for its ergonomically designed offices with adjustable desks and collaborative spaces, demonstrates a commitment to employee well-being. Furthermore, as technology becomes increasingly integrated into our work, understanding human-machine interaction is essential. Consider the design of aeroplane cockpits: prioritising clear visual displays and intuitive controls minimises human error and enhances safety, a principle applicable to any workplace utilising complex technology.
Managing Risk and Cultivating a Safety Culture: Preventing Human Error
Work psychology emphasises proactive risk management and the development of a strong safety culture. By identifying potential hazards and implementing robust safety protocols, organisations can minimise accidents and injuries. The “Swiss cheese model” of accident causation illustrates how multiple layers of defence, from engineering controls to safety training, are crucial for preventing errors. Understanding the psychological factors that contribute to human error, such as fatigue and stress, allows for the development of targeted interventions.
Motivating and Engaging Employees: The Psychology of Performance
Motivating and engaging employees is crucial for organisational success. Work psychology explores the complexities of motivation, drawing on theories like Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory, which distinguishes between hygiene factors (salary, working conditions) and motivators (achievement, recognition). Companies like Netflix, known for its emphasis on employee freedom and responsibility, leverage intrinsic motivators to drive performance. Recognising and rewarding employee contributions fosters a positive and motivating work environment.
Diversity, Inclusion, and Belonging: Creating an Equitable Workplace
Creating a truly diverse and inclusive workplace requires a conscious and ongoing effort. Work psychology provides guidance on implementing diversity and inclusion training programs that address unconscious bias and promote inclusive leadership. Microsoft’s diversity and inclusion initiatives, including employee resource groups and mentorship programs, demonstrate a commitment to creating an equitable workplace. By fostering a sense of belonging, organisations can attract and retain top talent from diverse backgrounds.
Age and the Evolving Career: Supporting Employees Across the Lifespan
Work psychology recognises the diverse needs of employees at different career stages. From young people entering the workforce to older employees navigating career transitions and retirement, understanding these unique needs is critical. Offering flexible work arrangements, mentorship programs, and opportunities for reskilling and upskilling can support employees throughout their careers. Companies like AARP offer resources and support for older workers, highlighting the importance of age-inclusive workplace practices.
Work Psychology: Unlocking Human Potential in the Workplace
Work psychology provides a crucial framework for understanding and optimising the human experience at work. By applying its principles, organisations can create workplaces where employees feel valued, engaged, and empowered. If you want to learn more and develop your skills we have a range of psychology and behavioural sciences programmes on offer for 2025/26.























